Blockchain Technology is a distributed database that creates an unchangeable digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual tokens that use cryptography to secure their transactions and control the creation of new units. Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, was created in 2009. There are three primary types of blockchain: public, private, and hybrid. We are going to discuss all three types in this blog.
Blockchain technology, the engine behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, has immense potential to change the world in ways we can’t even imagine today. But how will blockchain impact our future? In this blog, we’ll discuss the benefits and drawbacks of each type, as well as their applications outside the realm of cryptocurrency, including supply chain management and smart cities. To understand more about this exciting technology, continue reading below!
What is Blockchain Technology?
A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It constantly grows as “completed” blocks are added with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the blockchain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Bitcoin is a digital currency that uses blockchain technology to track transactions. All transfers are recorded publicly in a database called a blockchain. To create bitcoin, users must complete a complex online process known as mining, which involves using computers to solve complex math problems.
This process guarantees that bitcoins aren’t printed or minted to counterfeiters—there’s only so much of it available. Bitcoin buyers pay for their coins by electronically transferring conventional currencies across exchanges, where they can buy and sell bitcoins at market prices.
Also Read: Cloud Computing vs. Blockchain Technology: Which Is Right For Your Business?
How do Blockchain Works?
Blockchain technology uses a combination of cryptography and game theory to create a system of decentralized trust. Every blockchain comprises blocks organized into an immutable sequence. Each block contains two parts, the block header and the block content.
The block header contains metadata, such as the previous block’s hash in the sequence, to prove that it follows from this one. The block content comprises transactions or other information participants share in a transaction.
The most important thing to remember is that blockchain technology isn’t just about cryptocurrencies. It can build decentralized applications from currencies and voting systems to healthcare, insurance, and supply chain management systems. It’s also worth noting that not all blockchains are private or public.
What are the Uses of Blockchain?
There are a lot of potential uses for blockchain technology. Here are some popular use cases:
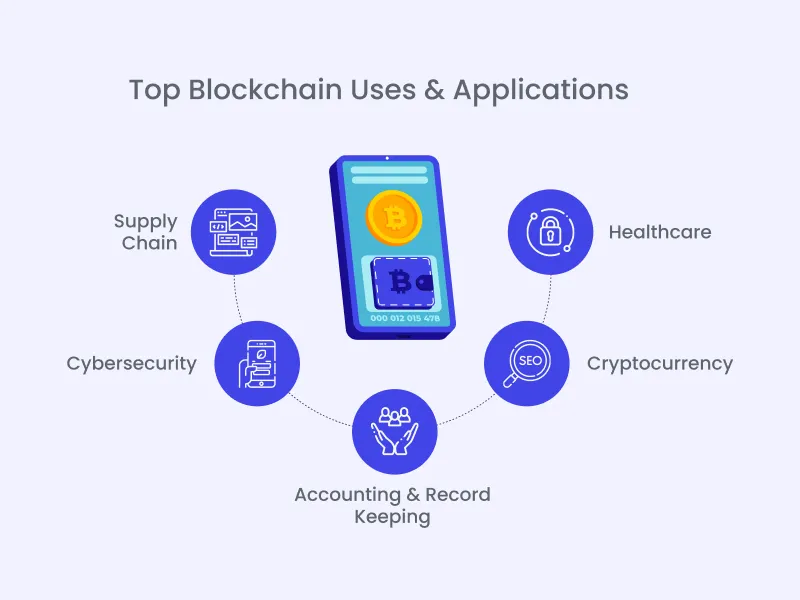
- Financial Services: Blockchain can streamline financial services. For example, it can settle transactions faster and more securely.
- Healthcare: Blockchain can help to secure patient data and protect privacy. It can also track medical records and prescriptions.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain. This can help to improve transparency and efficiency.
- Voting: Blockchain can create a secure and tamper-proof voting system. This might increase voter turnout and confidence in the results.
- Identity Management: Blockchain can securely verify identities and store personal data. This could have a major impact on reducing fraud and protecting people’s privacy.
What Is The Difference Between Private, Public & Hybrid Blockchains?
Below is a detailed comparison between Public, Private & Hybrid blockchain technology to better understand:
| Sr. No | Public | Private | Hybrid |
| Usage |
Public Blockchain is used for Bitcoin transactions because it is open to the public. |
Private Blockchain allows companies to keep a record of their transactions without needing a central authority. |
It is used for both public & private blockchains. It was developed to use the best aspects of both public & private blockchains. |
| Privacy |
It is open to everyone, and no one person is controlling them. |
Private Blockchain tends to offer higher levels of security due to the number of participants |
It offers companies the freedom to choose whether they want their transactions publicly verified. |
| Order of Magnitude |
The order of magnitude in public blockchain technology is much higher than that of private blockchain. |
The order of magnitude in private blockchain technology is significantly lower. |
In hybrid blockchain technology, the order of magnitude is relatively high. |
| Speed |
The speed of public blockchain depends on the number of people using it. It can take up to 10 minutes for a transaction to be confirmed. |
The speed of a private blockchain depends on the network’s number of nodes. The more nodes there are, the faster it will be. |
The speed of a hybrid blockchain can be anywhere from seconds to minutes. |
| Examples |
Bitcoin, Monero, Zcash, Dash, Litecoin, Stellar, Ethereum, Steemit, etc. |
R3 (Banks), EWF (Energy), B3i (Insurance), Corda. |
XinFin (XDC) |
The main difference between private, public, and hybrid blockchains is the level of access each type of blockchain provides. A private blockchain is permissioned, meaning only approved users can access it. A public blockchain is open to anyone who wants to join. A hybrid blockchain combines aspects of both private and public blockchains.
Private blockchains are well suited for enterprise use cases where there is a need for increased security and privacy. For example, a company may use a private blockchain to keep track of its financial records or employee data.
Public Blockchains are well-suited for use cases where transparency and immutability are important. For example, a public blockchain could track donations or store medical records.
We can use hybrid blockchains where privacy and transparency are essential. There are many different uses for blockchain technology. The type of blockchain used will depend on the specific use case.
Also Read: {Whitepaper / PDF} Blockchain: The Game-changer To Radically Transform Your Business
What Is A Private Blockchain?
We also referred to a Private Blockchain to as a permissioned blockchain. This is because it only allows a certain group of people to access it. These companies or organizations generally wish to use Blockchain Technology to create a distributed ledger system. We can use this to track products through the supply chain to manage transactions and records.
An example of a private blockchain is Hyperledger. Hyperledger is an open-source collaborative effort created to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies. It’s a global collaboration hosted by The Linux Foundation. Membership in Hyperledger is open to anyone with interest in participating.
IBM is a large contributor and has hundreds of employees working on its codebase daily. The benefits of Private Blockchains are:
- Private blockchains provide data privacy.
- Another benefit of private blockchain is increased security. With traditional centralized databases, there’s always the possibility that someone will hack into them and steal information.
- Benefit of private blockchain is security. With traditional databases, there is always a chance to get hacked, and hackers can steal your sensitive data.
- Private blockchain technology can be used for securing different transactions and for recording processes.
- Private blockchain technology helps hire blockchain developers and blockchain development companies.
- Many different industries are looking at the option of developing their private blockchain networks to serve their needs better.
What Is A Public Blockchain?
A Public Blockchain is a permissionless blockchain where anyone can join and participate in the network. This type of blockchain is decentralized, meaning no central authority manages the network. Instead, the network is managed by all the users collectively.
Bitcoin is the best-known example of a public blockchain. Anyone can join the Bitcoin network and start participating in the Bitcoin ecosystem. There are no barriers to entry, and no one needs permission to join.
Private blockchains are much more limited than public ones. Access to a private blockchain is typically restricted to institutions with permission to use it. The ledger is not as transparent because only a select few can view it. A blockchain may be private or public.
It all depends on who can view it, who owns it and whether it’s centralized or decentralized. Below are the benefits of public blockchain technology:
- It is open to everyone, and no one controls them. You also notice that many people would like to hire blockchain developers.
- Public blockchain networks offer higher levels of security number of participants
- Public blockchain offers greater levels of security due to a large number of participants.
- It has lower fees, which makes sense, considering many people are helping verify transactions. For example, Bitcoin (a cryptocurrency) has had low fees for years now, which helps encourage people to spend their coins.
- You don’t need a central authority or middleman to act as an intermediary between two parties. Transactions don’t require escrow agents because the entire process is automated and peer-to-peer.
- Public blockchain technology can help reduce fraud risk since it records every transaction, including when money was sent, how much was sent, where the money came from etc.
Also Read: Here’s Why Should Enterprises Adopt Blockchain For Digital Assets In 2022-23?
What Is A Hybrid Blockchain?
A hybrid blockchain is a type of distributed ledger that combines characteristics of both private and public blockchains. A hybrid blockchain can be either partially or fully public, but it must always be permissioned, meaning only authorized users can access it.
The major advantage of a hybrid blockchain is that it allows for the best of both worlds: the security and privacy of a private blockchain with the transparency and immutability of a public blockchain. This makes hybrid blockchains ideal for applications that require both confidentiality and audibility. Below are the benefits of hybrid blockchain technology:
- It gives companies the freedom to choose whether they want their transactions publicly verified. If a company wants its transaction to be publicly verified, then it can choose to set up its node and make its transactions publically available.
- Hybrid blockchain allows businesses to control how many nodes in their network verify transactions, so if one server goes down, the others will continue verifying transactions.
- One of the most significant benefits of using a hybrid blockchain network is flexibility, as you get all the advantages from both types of blockchain networks without any disadvantages.
- There are no limitations concerning scalability, so the system can support billions and trillions of users worldwide.
- Hybrid blockchain technology security becomes even stronger because multiple copies exist simultaneously each time a new block gets mined (or added). Thus making hacking nearly impossible.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Each Type Of Blockchain
- Decentralized Public Blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are permissionless, meaning that anyone can participate in the network and help to validate transactions. This makes them very secure, as it is challenging for a single entity to take control of the network. However, this also means that public blockchains are slow, as there can often be a lot of congestion on the network.
- Private Blockchains are permissioned, meaning that only certain users are allowed to access and validate transactions on the network. This makes private blockchains much faster than public ones, as there is less congestion on the network. However, this also means they are less secure, as it is easier for a single entity to take control of the network.
- Hybrid Blockchains combine features of both public and private blockchains to create a more balanced approach. For example, a hybrid blockchain could be permissionless for general use but have certain sections that are only accessible to certain users. This would give the hybrid blockchain the benefits of both public and private blockchains.
Also Read: How Has Blockchain Evolved FinTech For 2024?
Uses for Private, Public, and Hybrid Blockchains
There are various ways to use private, public, and hybrid blockchains. Some of the most common uses are:
Private Blockchain Technology
With private blockchain technology, all of your transactions remain fully confidential. There’s no need to worry about protecting your data from prying eyes because you control who has access to it. This is one of the most common uses for private blockchain technology. This technology can also be used when you want to follow the rules unique to your company or industry. Moreover, the potential use for private blockchain technology is as a tool for identity management.
Another use for private blockchain technology is for improving data integrity. For example, if you’re an eCommerce platform that relies on third-party vendors to provide your products, you can use a private blockchain to verify inventory levels at each step in your supply chain.
Public Blockchain Technology
Private blockchains are often used for enterprise applications where the participants are known and trusted. Private blockchains can offer improved security and privacy over public blockchains.
It is often used for cryptocurrencies, where anyone can participate. Public blockchains offer censorship resistance and security through decentralization.
For example, in a public blockchain, the whole world can see the transactions happening in the shared database. However, in a private or permissioned blockchain, transactions are only visible to those permitted by the node’s operator or through their unique cryptographic key (i.e., whitelisted).
A Blockchain Development Company should always research before building it to ensure it will meet all of your needs going forward.
For instance, if you have an idea for a blockchain app that stores names and social security numbers but would like people to access it anonymously, then you’ll probably want to hire blockchain developers with an understanding of cryptography.
Hybrid Blockchain Technology
Likewise, in a hybrid or permissionless system, some nodes are open for everyone to participate. Others require approval from one of the administrators before they become active on the network.
Hybrid blockchain technology is generally used for specific tasks or functions that are too private to share. For example, a hybrid blockchain can be created where two blockchains operate simultaneously.
One would be public, open, and accessible by anyone; the other would remain private, with limited access only available to those who have been granted permission.
Hybrid blockchains are especially valuable in scenarios where privacy and transparency are required, such as in blockchain Decentralized Marketplace applications, where users want a combination of public verification with some degree of restricted access for sensitive business transactions.The same company might want one of its databases to be public so that everyone can see the list of all employees, but they may not want everyone to know what their payroll records look like, so they’ll use the second blockchain instead. A Blockchain Development Company will help you set up the transaction between both blocks. You can also choose if either blockchain has moderators in charge of verifying transactions, updating new blocks into the chain, and deleting obsolete ones.
Also Read: Top Blockchain Development Companies to Improve Your Business Efficiency
What are Side Chains?
Side chains are blockchain networks that connect to the main chain. They are connected to the main chain through a two-way peg. A sidechain is a separate blockchain where units of value, or coins, are transferred between different blockchains.
Users can transfer their coins from the original blockchain to the sidechain and vice versa. This is achieved by locking up coins on one blockchain to mint new ones on another.
One of the side chains’ most prominent use cases is extending blockchain functionality. For example, Bitcoin’s scaling issue can be addressed by moving transactions from its main chain into a sidechain.
Shorter transaction time, enhanced privacy and asset tokenization are just a few examples of blockchain functionality that could be made possible through side-chain implementation.
Conclusion
Private, public, and hybrid blockchains have unique benefits and drawbacks that make them suitable for different use cases. Private blockchains are great for companies or organizations that need to keep their data confidential.
Public blockchains are better suited for applications that need to be decentralized. Hybrid blockchains combine the best of both worlds by allowing privacy and decentralization. Ultimately, your type of blockchain will depend on your specific needs. To understand better, you can Hire Blockchain Developers from the leading IT company Valuecoders. We have a team of experts who can help you explore business prospects.